What Is Thermal Bridging and Why Does It Matter?
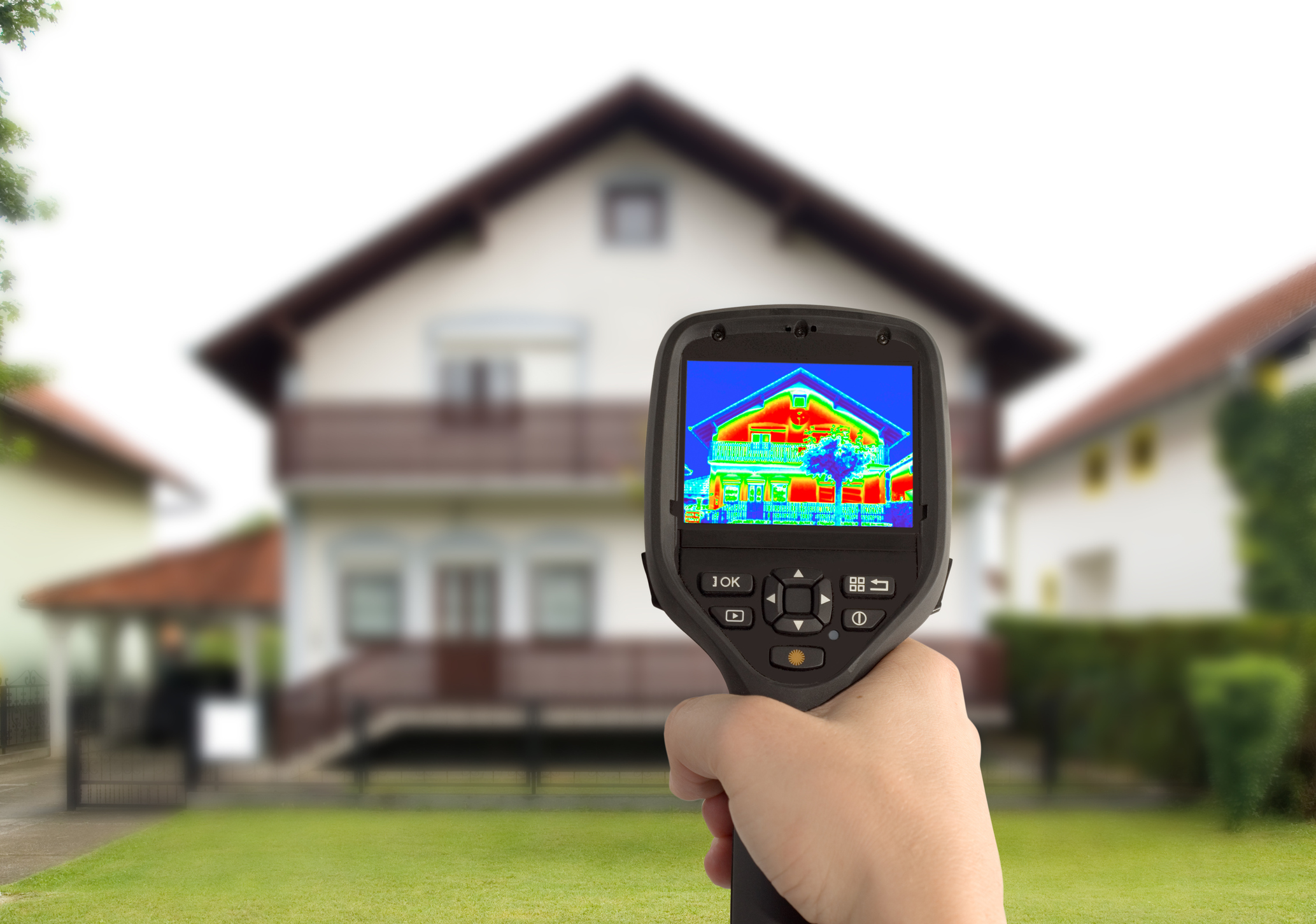
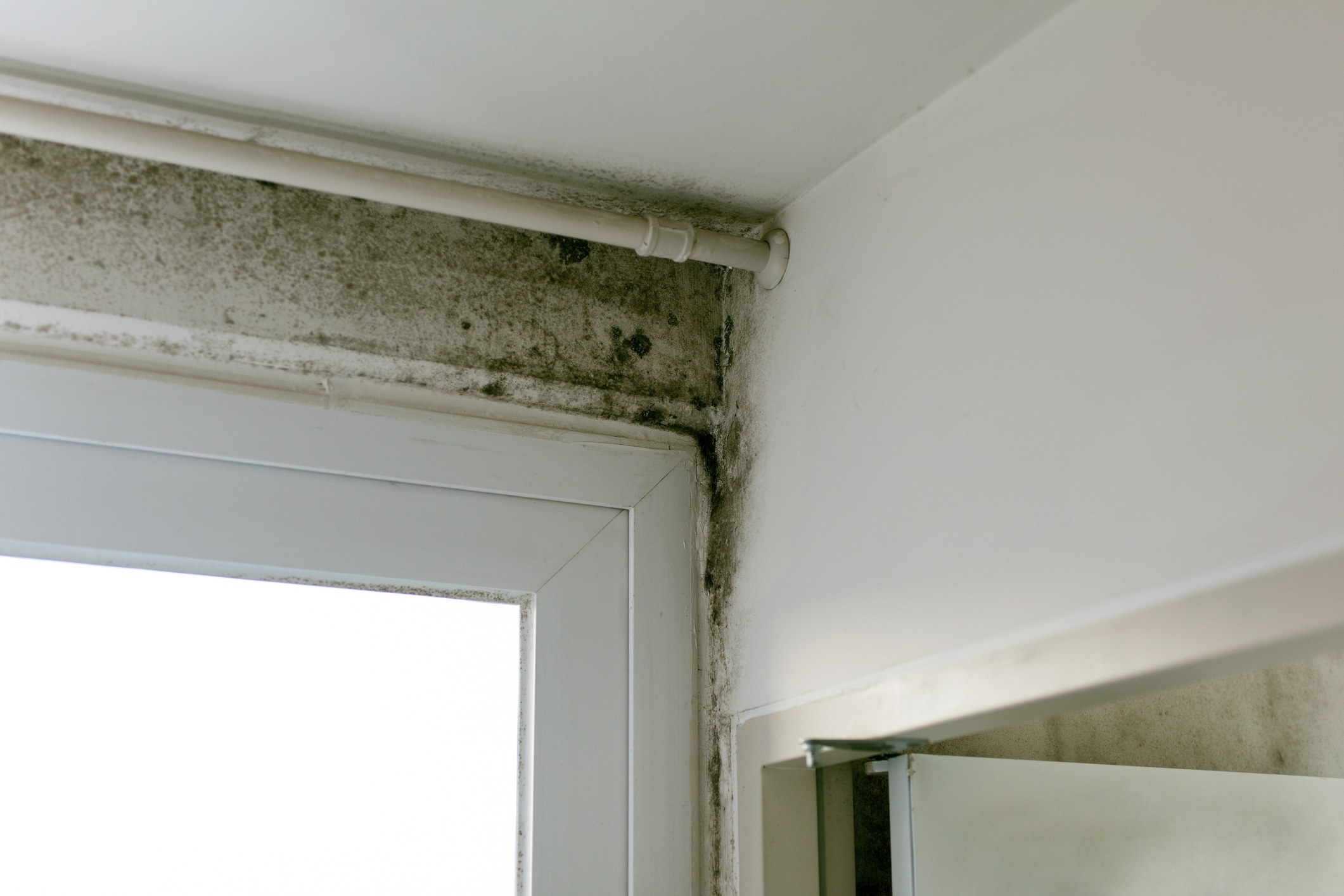
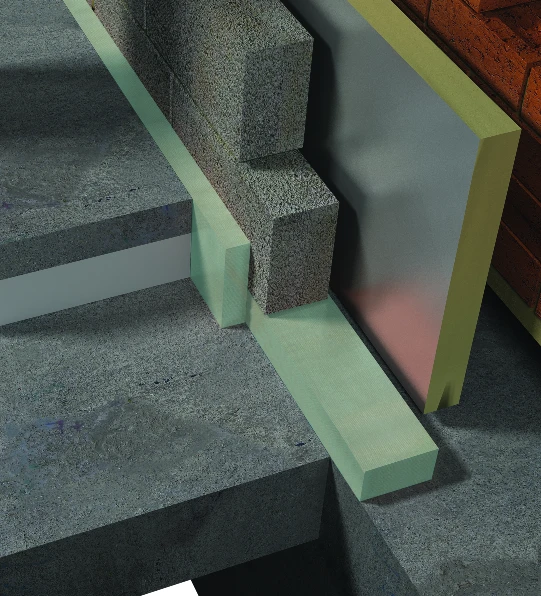
To understand more about how, why and where thermal bridging occurs, we firstly need to look into different building connections outlined in the very initial stages of a construction project. The bridging occurs when heat passes through a material that is more conductive than the materials around it, causing a transfer of energy, so any connections where this is a possibility need to be carefully considered.
Thermal bridges reduce efficiency by bypassing any insulation which acts as a ‘bridge’ for energy, creating spaces that cannot hold temperatures. Thermal breaks are durable, effective and, most importantly, cost effective solution to thermal bridging.
Where Is Thermal Bridging Most Likely to Occur?
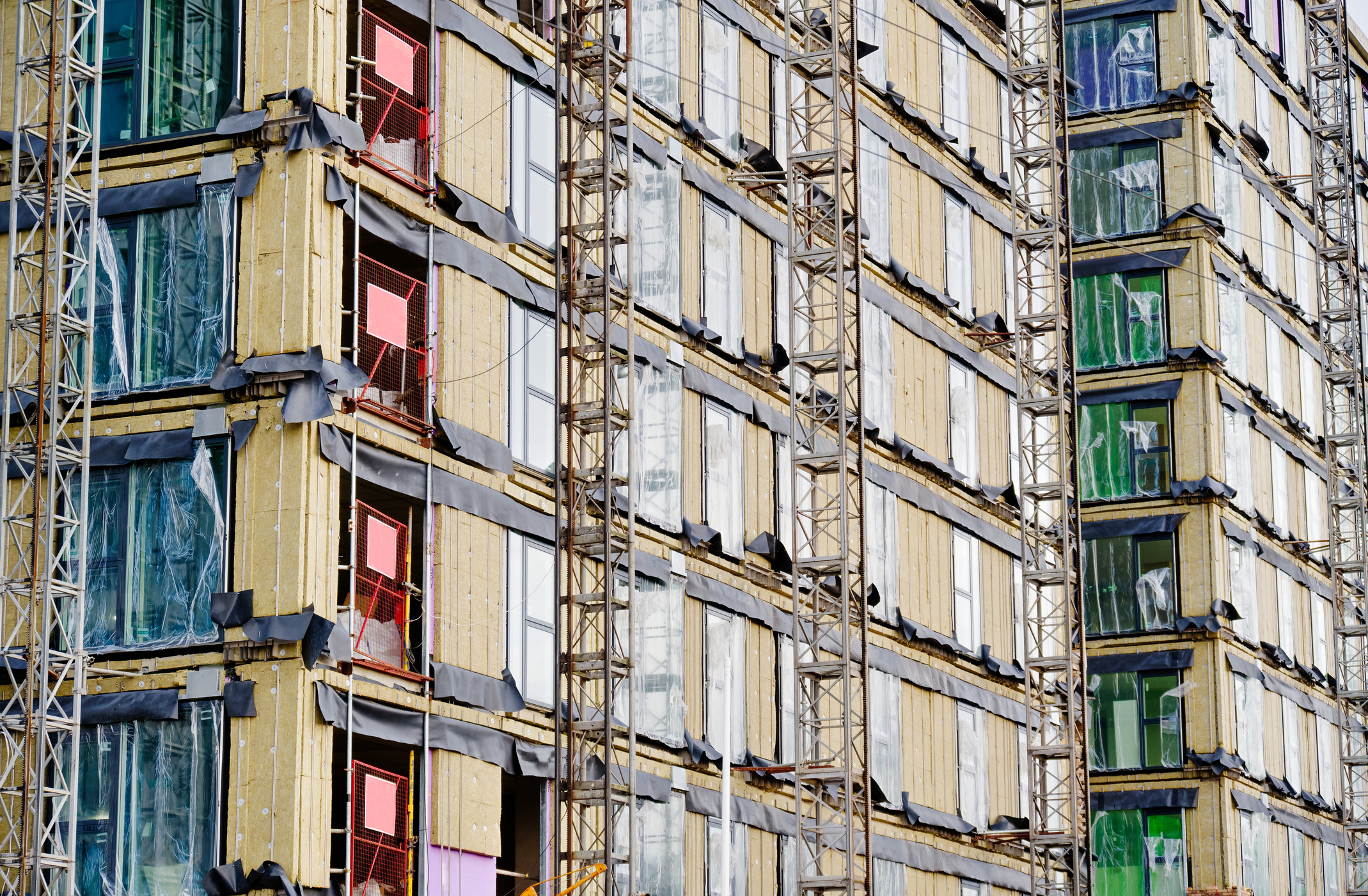
Applications where thermal bridging is most likely to occur includes masonry shelf angles, column bases, foundation walls, balcony / canopy installations, roof penetrations and cladding attachments. These are key areas where energy-saving thermal breaks are essential to the efficiency of the building.
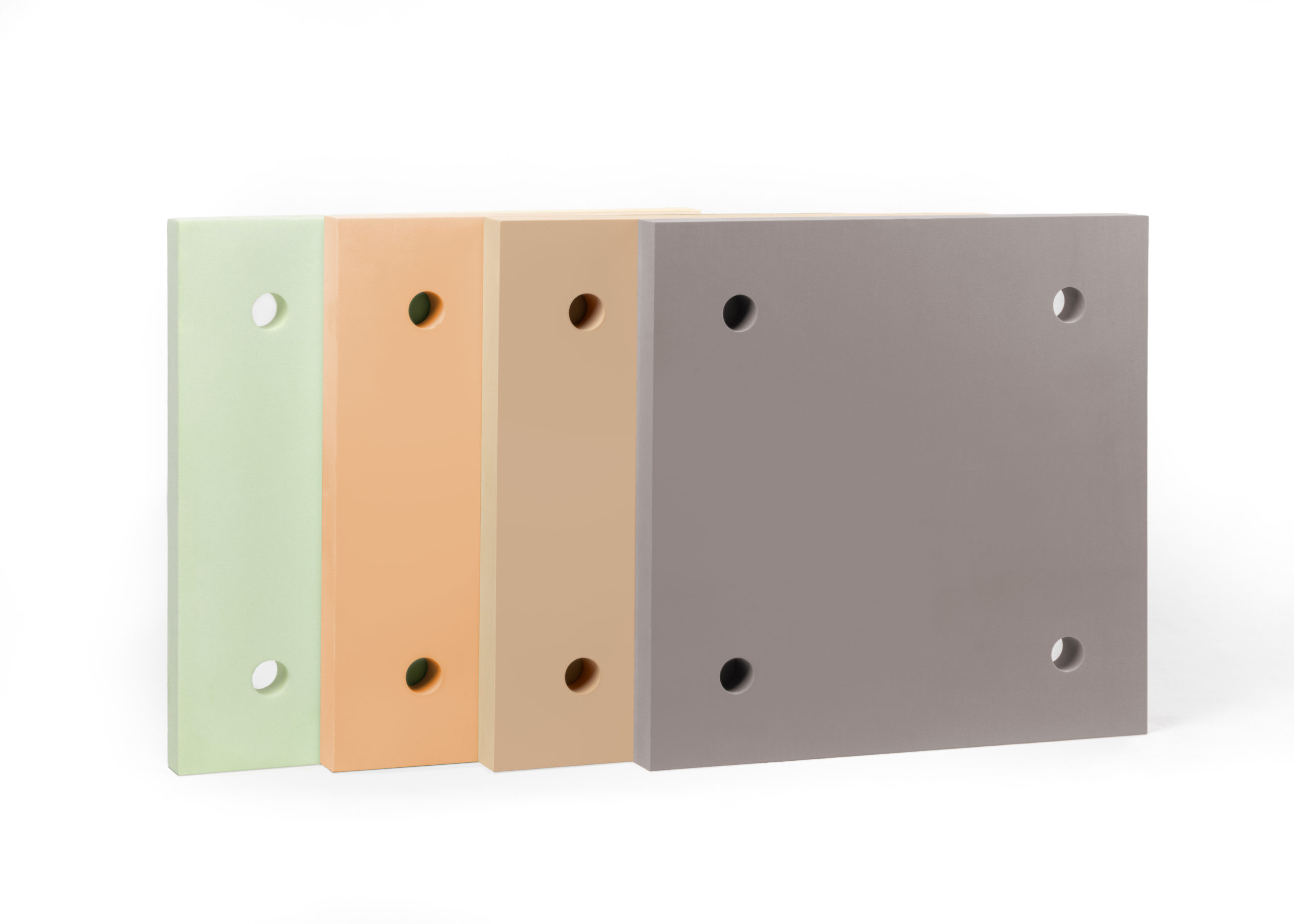
Thermal break materials can be used anywhere that a transition exists within the building envelope. The revolutionary solutions work by isolating the temperatures using an inert, closed-cell polymer, which has an ultra-high density. This ensures that the thermal break solution is not only insulating and water resistant but strong, which, when working with steel, is often a requirement due to the high-load capacity of the overall structure
Why Is Steel Common in Construction Despite Thermal Risks?
The advantage of using steel as a building material in construction projects has long been recognised by designers and specifiers, making it a revolutionary material within the building sector. The most traditionally used material for commercial constructions, it is favoured due to its ability to bind well to concrete, it is strong and relatively cost effective, and so, specified for a large range of building projects. With an approximate 90% market share for single-storey industrial buildings, its strength and versatility are big selling points, although thermal conductivity and performance isn’t always considered.
To learn more about the effects of thermal bridging and Armatherm’s thermal break materials, please contact Armatherm and the team using the details on our contact us page.